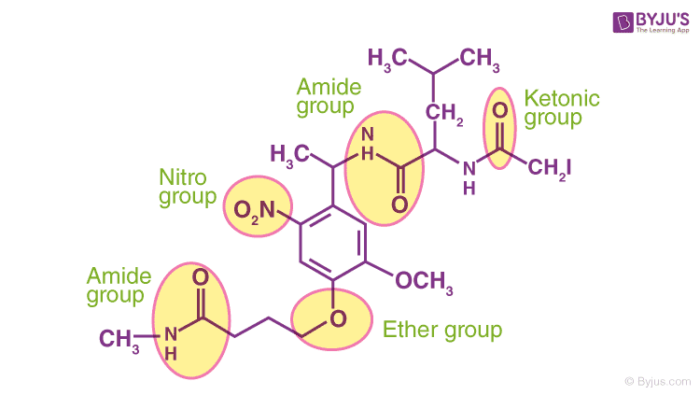
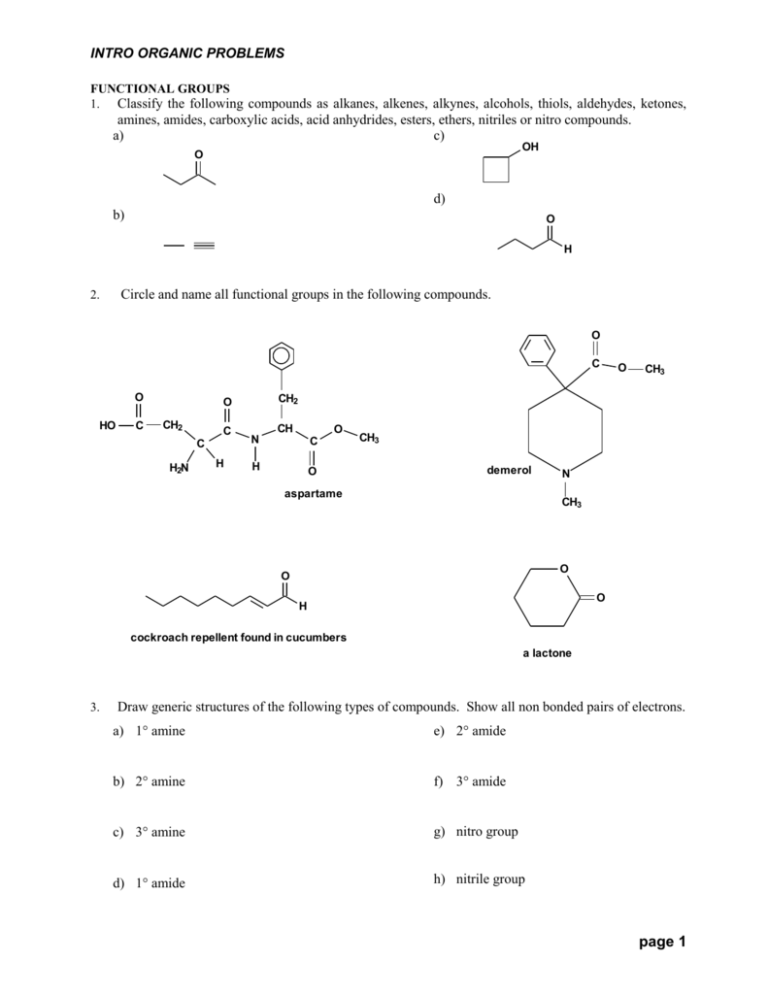
1) Give the name of the functional group indicated in the molecules below for Fl You do not have to do AE or J CH3 N HN H₂Ñ OCH3 ОН N H3C а inkage) I sildenafil (Viagram) h aspartame (artificial sweetner) 2) Please draw structures for compounds named below A) 1chloro3ethylhexane B) 5tertbutyl1,2dichloro2,3dimethyloctane 3 Common name 1) Name the alkyl group in alphabetical order and then add the word amineIn case the two alkyl groups are same, the numerical prefix di is used before the name of the alkyl group 2) Add the prefix Nalkyl before the name of the aminoalkane ;N,NDimethylformamide HCON (CH3)2 PubChem
Http Www Chem Latech Edu Upali Chem121 Notes C17 121 Pdf
N(ch3)2 functional group name
N(ch3)2 functional group name-Secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) CH3CH2CH2 N H H CH3 N CH3 CH3 CH3CH2CHCH3 NH2 CH3CH2 N H CH3 N H N 6 Nomenclature of Amines • Simple 1°, 2°, and 3° amines common (trivial) names are obtained by alphabetically arranging the names of the alkyl substituents on the nitrogen and adding the suffix amine (eg, ethylmethylamine) Find an answer to your question Name a functional group present in (i) CH3CHO, (ii) C2H5COOH Bubbiya8monika Bubbiya8monika CBSE BOARD X Secondary School answered Name a functional group present in (i) CH3CHO, (ii) C2H5COOH 2




I 10 Identify The Functional Group Of The Following Compound Ch3 C H
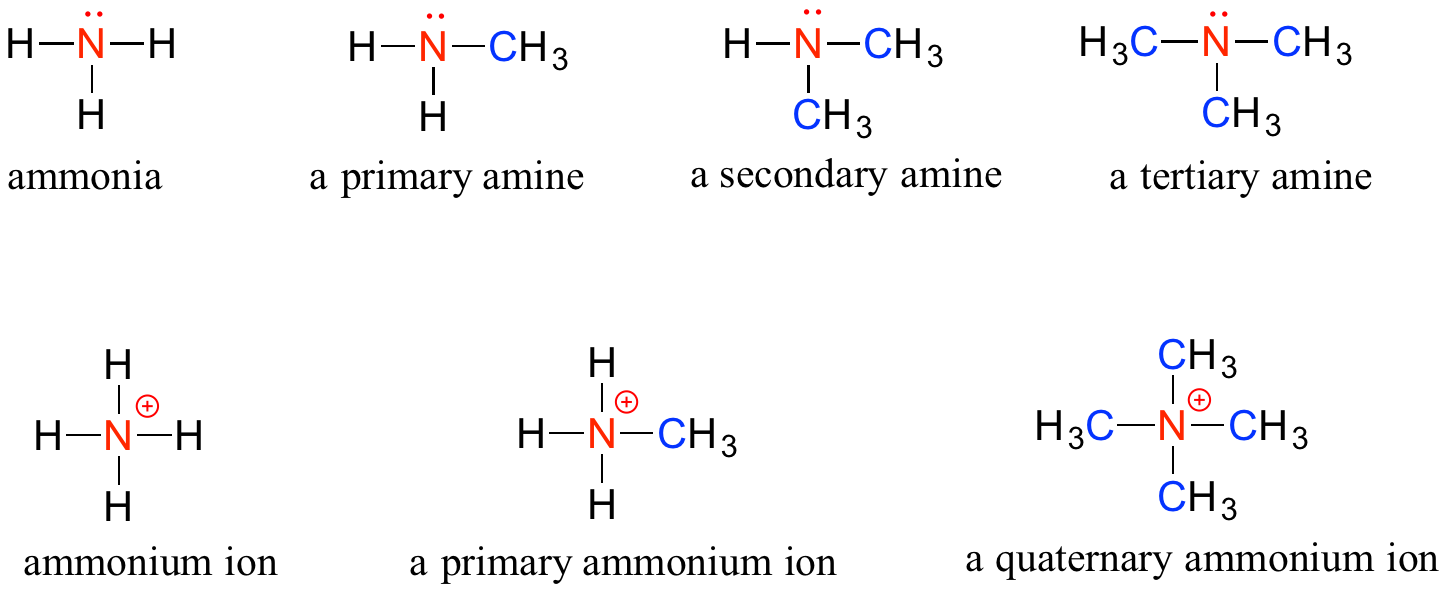
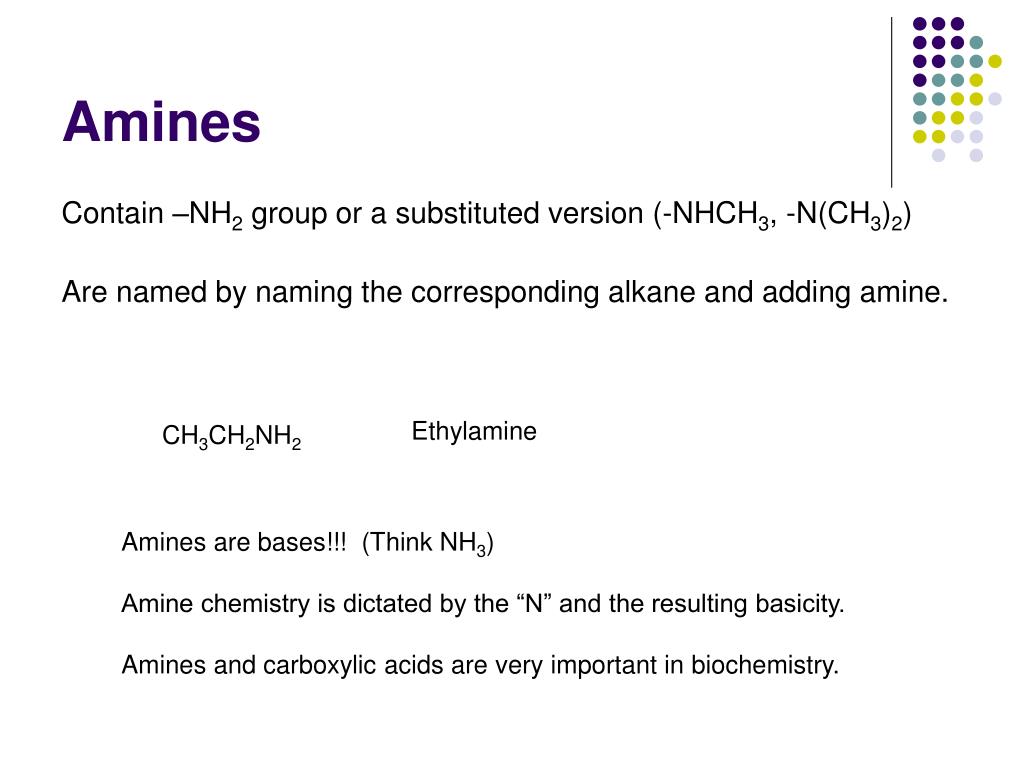
• contain an "amino" group – a N atom bonded to 1, 2, or 3 carbon atom groups by single bonds H Aldehydes and Ketones • contain a C=O ("carbonyl") group • note that in condensed structural formulas, the aldehyde group may be written as –CH=O or as –CHO I Carboxylic AcidsCH 3 CH 3—CH 2—NH 2 CH 3—NH—CH 3 ethylamine dimethylamine CH 3—N—CH 2—CH 3 ethyldimethylamine Name the following amines IUPAC Names of Amines • Amines are named as alkanamines • The –e in the alkane name of the longest chain is changed to –amine NH 2 • The chain is numbered to locate the amine group and substituents CH 3—CH 2—NH 2 CHFUNCTIONAL GROUPS and Their Names Compound type Functional group Simple Example Name ending Alkene (double bond) CH 3CHCH 2 Propeneene Alkyne (triple bond) CH 3CCH Propyneyne Arene (aromatic) Benzene None Halide X = F Cl, Br, I CH 3CH 2I Iodoethane or Ethyl Iodide None Alcohol CH 3CH 2OH Ethanolol Ether CH 3CH 2O CH 2CH 3 Ethoxyethane or
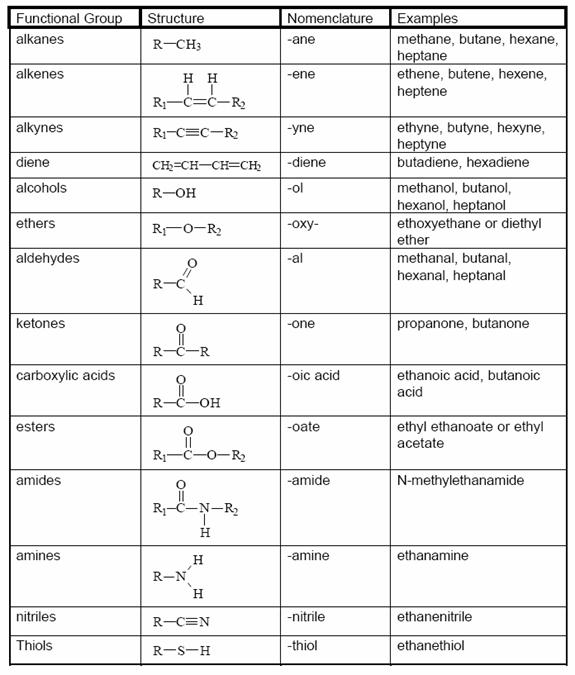
Organic molecules are also named using the functional group approach 2hexanone 2hexanol 2chlorohexane The rule is that functions assume their distinct identity when separated by –CH2– groups Thus, the carbonyl, C=O, and hydroxy, OH, of a carboxylic acid, RCOOH, are part of a single function and are NOT "alcoholplusketone"Chapter 3 Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers 2 3 Alcohols 4 The Hydroxy (—OH) Functional Group •The hydroxyl group (—OH) is found in the alcohol and phenol functional groups (Note that's not the same as hydroxide, OH, which is ionic) –in alcohols, a hydroxyl group is connected to a carbon atom –in phenols, —OH is connected to a benzene ringC Functional Groups Compound Classification Compound Classification CH 3 —OH alcohol CH 3 —NH 2 amine O CH 3 —C—NH 2 amide carboxylic acid H 2 C CH 2 aldehyde CH 3 —O—CH 3 ether ketone carboxylic acid Q7 Classify each of the following according to its functional group a alkene CH 3 —CH 2 —CH=CH—CH 3
Study Notes The concept of functional groups is a very important one We expect that you will need to refer back to tables at the end of Section 31 quite frequently at first, as it is not really feasible to learn the names and structures of all the functional groupsAmides (RCONH 2) take the suffix "amide", or "carboxamide" if the carbon in the amide group cannot be included in the main chainThe prefix form is both "carbamoyl" and "amido" Amides that have additional substituents on the nitrogen are treated similarly to the case of amines they are ordered alphabetically with the location prefix N HCON(CH 3) 2 is N,NCH 3 CH 2 NHCH 2 CH 3;



Pdfs Semanticscholar Org 2f22 49bce2cdf55e77ddbdefd87 Pdf




I 10 Identify The Functional Group Of The Following Compound Ch3 C H
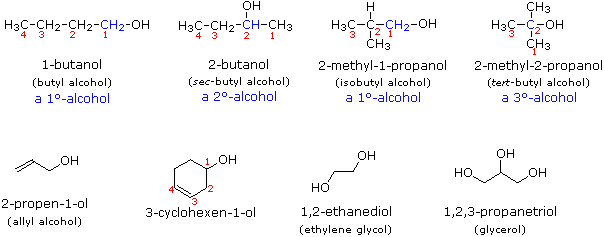
General Information Alkane Names & Functional Groups Alkane Names Primary, Secondary, Tertiary & Quaternary Carbons Common Functional Groups Download pdf Alkane Names Number of carbons (n) Name Formula ( C n H 2n2) 1 methane CH 4 2 ethane C 2 H 6 3 propane C 3 H 8 4 butane C 4 H 10 5 pentane C 5 H 12 6 hexane C 6 H 14Alcohol CH3CH2CH2OH ether CH3CH2OCH3 aldehyde CH3CH2CH2CHO ketone CH3COCH3 carboxylic acid CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH ester CH3CH2COOCH3 amine (2*) CH3CH2NHCH3 The common formula of ether is Cn H2nO, which satisfy the general formula of alcohol So the functional isomer of ether is obviously alcohol compound with functional group –OH Now, CH 3 CH 2 – O – CH 3 compound contain three carbon atoms Hence the molecular formula of the isomeric alcohol would be C3H8O and the name of the alcohol is




Quiz 2 Organic Chemistry I Chem 232 Docsity



Dimethylbenzylamine Wikipedia
(a) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH (b) CH 3 CH(OH)CH 3 (c) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CHO (Note This is one way to write an aldehyde) (d) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 (e) none of the above 6 Which of the following compounds is a functional group isomer of C 2 H 5 OH, ethanol (ethyl alcohol)?The blue atom is the nitrogen atom Notice in methylamine the carbon atom of the methyl group is bonded to the nitrogen In amines the nitrogen atom alway has three bonding groups and one lonepair amine (CH 3) 2 NH dimethylamine In this example of an amine two R groups are bonded to the nitrogen amine (CH 3) 3 N trimethylamineTable 12 Common Functional Grou Name Functional Group Example Acyl halido Alcohol Aldehydo Alkano Alkono Alkyl halide Alkyno Amido AmineEx;cELH #H;cc)c=c(;cxC=CEN(;cN(Aromatic ring @ Carboxylic acid jgow Diene )C=CC=C(E star j8pe Ethor CPLC Kotono Cgc Nitrjl® CC=N Organomotallic CM cH38§E H3CELH H3Cj8H H3CCH3 H2C=CH2 H3C



Functional Groups And Classes Of Organic Compounds Names Nomenclature Properties With Videos



Http Www Cpp Edu Psbeauchamp Pdf Fg Worksheet Pdf
Functional Groups A functional group is a defined grouping of atoms in an organic molecule A given functional group exhibits a characteristic set of chemical properties, which are largely independent of the rest of the structure of the molecule in which it is foundOrganic Functional Group List Functional Group Compound Prefix/Suffix Example IUPAC Name (Common Name) RH alkane ane CH 3CH 3 ethane CC alkene ene H 2C=CH 2 ethene (ethylene) CC alkyne yne HC≡CH ethyne (acetylene) RX haloalkane halo CH 3Cl chloromethane ROH alcohol ol (hydroxy) CH 3OH methanol RNH 2 amine amine (amino) CH 3CH 2NHEthyl ether CH 3CH 2OCH 2CH 3 not so polar (symmetric) some lipids esterCOOR methyl ester of acetic acid CH 3COOCH 3 polar not charged fats (eg, triglycerides) detail O COR amideCONH 2 acetamide CH 3CONH 2 polar, not charged proteins (eg, asparagine) detail O CNH 2 sulfhydrylSH 2mercaptoethanol HOCH 2CH 2SH



Nanopdf Com Download Chapter Carboxylic Acids And Nitriles Pdf



Alcohol Reactivity
Elimination Alkenyl halides CH 2 =CHCl Chloroethene or vinyl chloride Electrophilic addition;4 Thiols and Amines H3CC OH CH3 H OH H3CC SH CH3 H SH H3CC NH2 CH 3 H N CH3 CH alcohols thiols amines Ethers The etherfunctional group is described as an sp3oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms, and may be symbolized as ROR' R and R' may be the same groups or different CH 3CH 2O CH CH CH3 O C CH3 CH3 CH3 O CarbonylContaining Functional A methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms — CH3 In formulas, the group is often abbreviated Me Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds It is a very stable group in most molecules While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, it can be found on its own in any of



Problems On Functional Groups And Chemical Bonding Organic Chemistry




Condensed Formulas What Do The Brackets Mean Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry Chemistry Lessons
Propyl The reaction for the combustion of heptane isWhich one of the following compounds is an isomer of CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH?The functional group here is amine and it's 2nd suffix is amine only so amine is written after the main chain name and main chain name is Meth as it contain 1 carbon Here 1st suffix is anewe have removed the' e ' from ane because the 2nd suffix ( amine) starts with a vowel and it contains 2 methyl group that's why it's written dimethyl in the prefix



Www Babcock Edu Ng Oer Lecture Notes Chemistry Chem 212 organic chemistry ii Pdf




Lecture2 123 101 Pdf Document
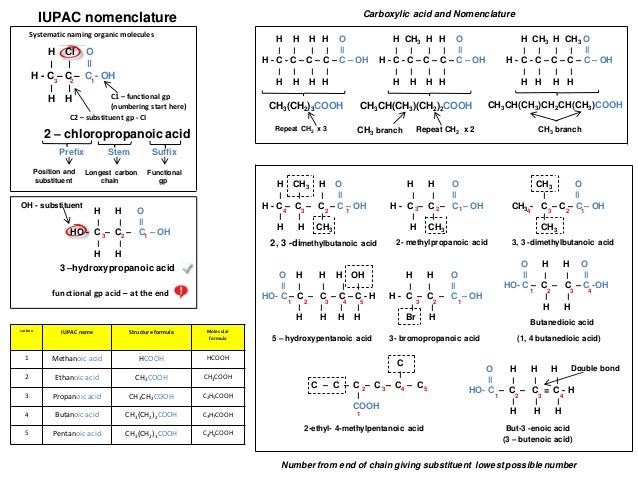
CH3O CH3CHCH2COH pentanoic acid 2methylbutanoic acid O 3methylbutanoic acid O 2methyl butyric acid O 2methyl4butanoic acid Esters are formed from the reaction of an ether with a carboxylic acid CH3NCH2CH3 CH3 True False The common name of CH3CH2OCH2CH3 is dimethyl ether diethyl ether(1) the hybridization about carbon is sp² Give the IUPAC name of (a) (CH 3) 2CHCH 2CH 2CH 3 (b) (C 2H 5) 2C(CH 3)CH 2CH 3 (c) 3 CH 3CH 2CHCH 2CHCH 2CH 3 CH CH 2CH CH 3Esterification Phenols C 6 H 5 OH Phenol




Slides Show



Labs Chem Ucsb Edu Zakarian Armen 03 03 Lecture 02 02 18 Pdf
Functional Group Molecular Formula IUPAC name general name/ Structure Characteristics Alkanes CH4 methane all single bonds (sigma) C2H6 CH3CH3 ethane sp3 hybridized HCON(CH3)2 N,Ndimethylmethanamide generally soluble in water CH3CONH2 ethanamide acetamide O OH O OCH 2 CH 3 O O O NH 2 NH 2 OOrganic Chem Function Groups And Names by lokisare9 , Sep 07 Subjects chem functional groups organic Click to Rate "Hated It" Click to Rate "Didn't Like It" Click to Rate "Liked It" Click to Rate "Really Liked It" Click to Rate "Loved It" 45 1Problem Set 2 Hydrocarbons and Functional groups ANSWER KEY Chemistry 260 Organic Chemistry 1 Which of the following statements about ethane is true?
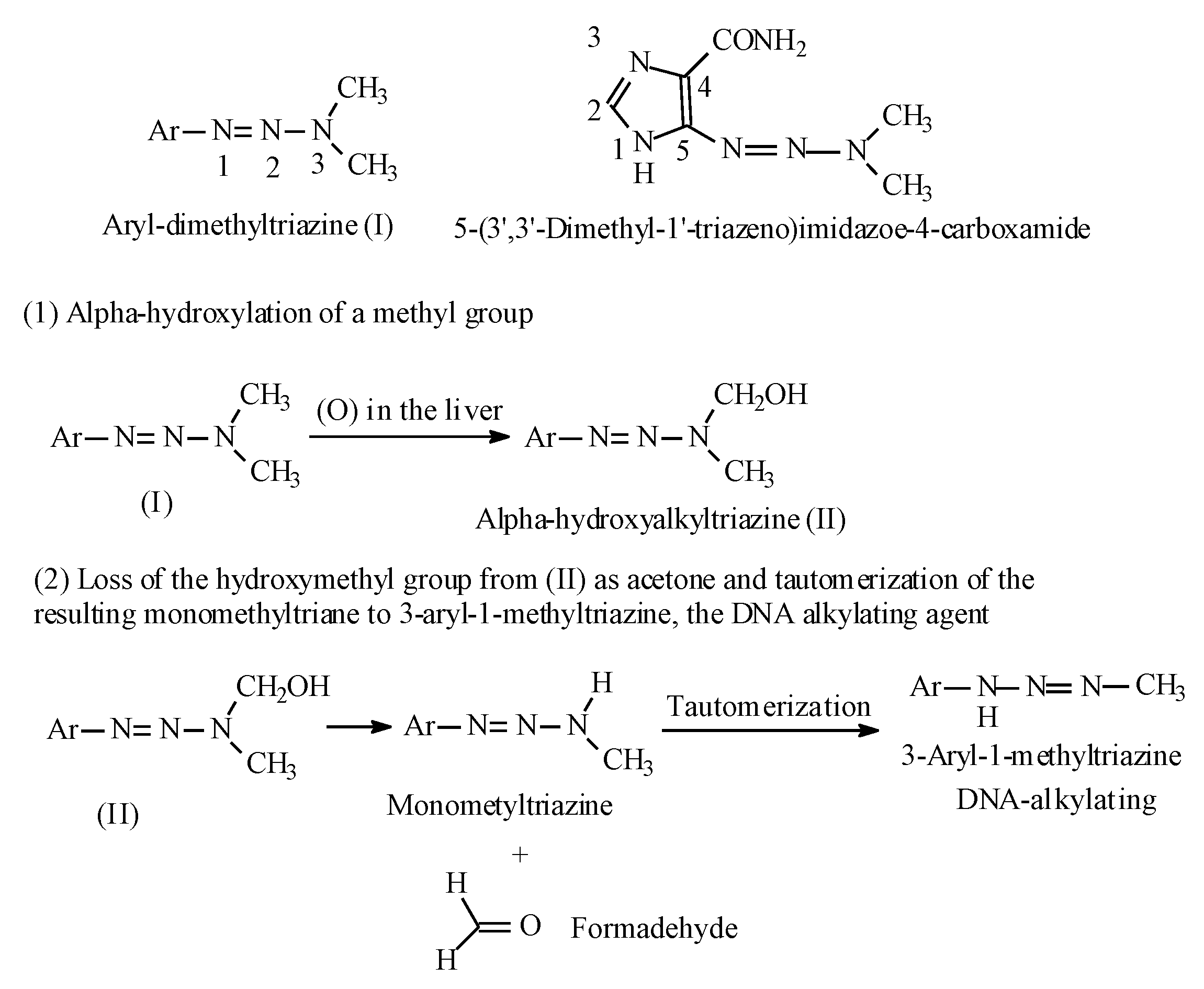



Molecules Free Full Text Metabolic Hydroxy And Carboxy Functionalization Of Alkyl Moieties In Drug Molecules Prediction Of Structure Influence And Pharmacologic Activity Html




Ch 3 Review Nomenclature Organic Compounds Compounds Of Carbon Organic Chemistry If They Have Only C And H Hydrocarbons E G Alkanes Methane Ch Ppt Download
What is the IUPAC name of CH3CH2CH2CH2N(CH3)2?Functional Group Name Example Alkane CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 (propane) Alkene CH 3 CH=CH 2 (propene) Alkyne CH 3 C CH (propyne) F, Cl, Br, or I Alkyl halide CH 3 Br (methyl bromide) Alcohol CH 3 CH 2 OH (ethanol) Ether CH 3 OCH 3 (dimethyl ether) Amine CH 3 NH 2Trimethylamine is a tertiary amine that is ammonia in which each hydrogen atom is substituted by an methyl group It has a role as a human xenobiotic metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite It is a tertiary amine and a member of methylamines It is a conjugate base of a trimethylammonium




Unodc Bulletin On Narcotics 1951 Issue 2 005



Ib Chemistry On Organic Nomenclature And Functional Groups
The eponymous member of this grouping is the carboxylic acid functional group, in which the carbonyl is bonded to a hydroxyl (OH) group As the name implies, carboxylic acids are acidic, meaning that they are readily deprotonated to form the conjugate base form, called a carboxylate (much more about carboxylic acids in Chapter )9146 PEG average M n 5000, PDLLA average M n 000\ ch_3ch_2n(ch_3)ch_2ch_3 {/eq} IUPAC name During the naming of compound involving amine functional group, the parent chain will be the one which have more number of carbon atoms




Identifying Functional Groups Video Khan Academy
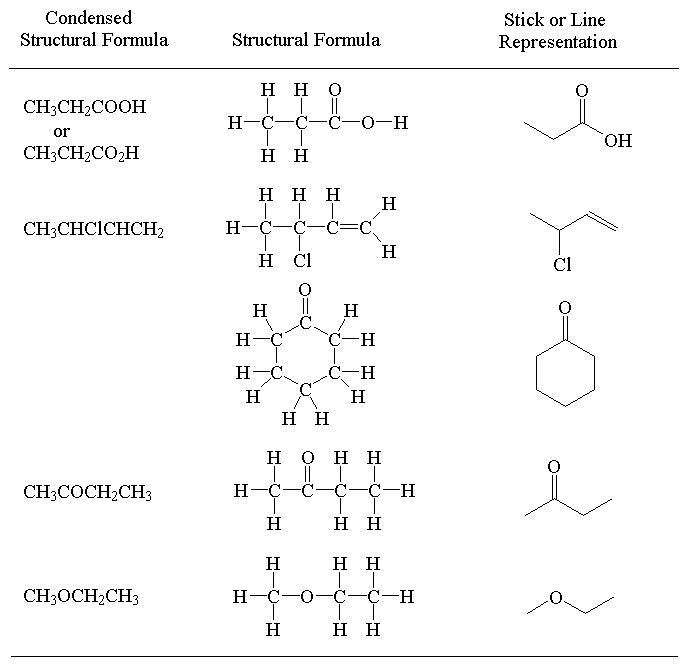



1
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 NHCH 3;A carboxyl group (COOH) is a functional group consisting of a carbonyl group (C=O) with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to the same carbon atom Carboxyl groups have the formula C(=O)OH, usually written as COOH or CO 2 H Carboxylic acids are a class of molecules which are characterized by the presence of one carboxyl groupSolution There is only one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen atom, so the amine is primary A group of three carbon atoms (a propyl group) is attached to the NH 2 group through an end carbon atom, so the name is propylamine There are two methyl groups and one ethyl group on the nitrogen atom
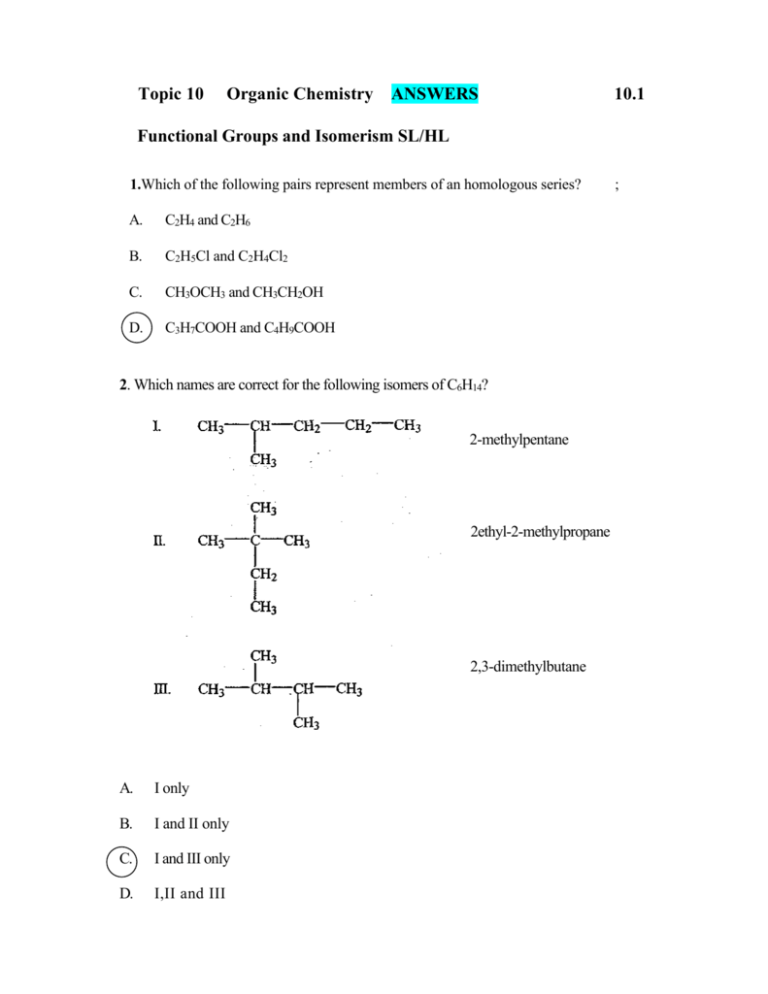



Topic 11 Organic Chemistry
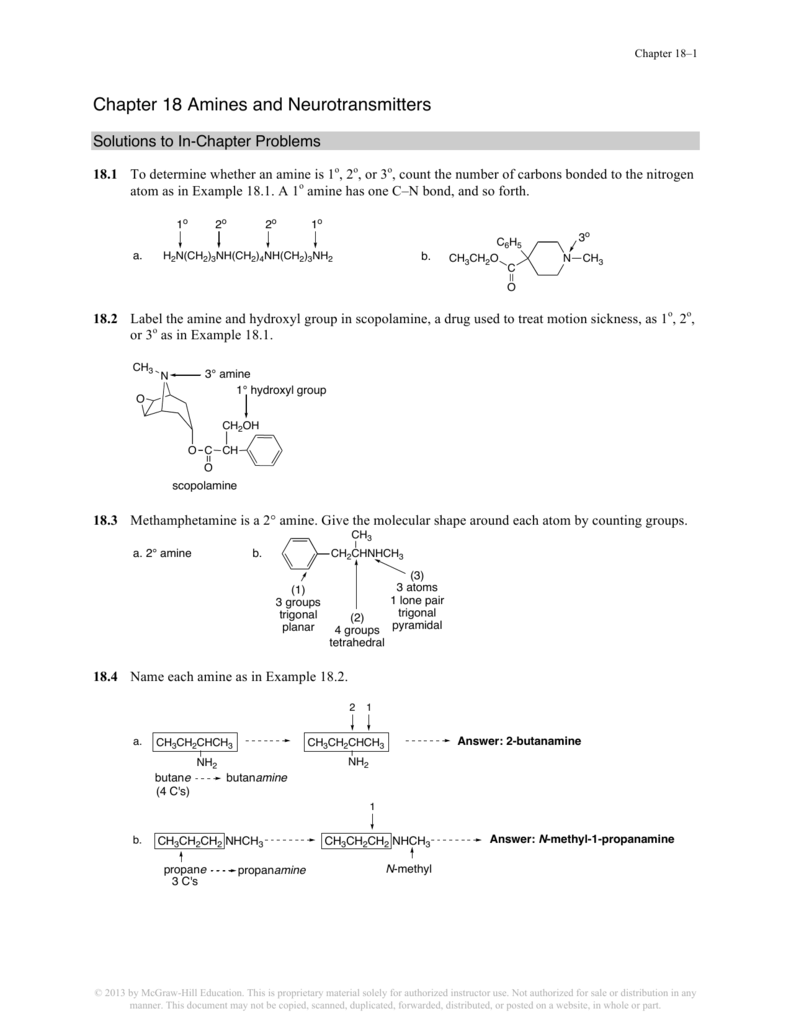



Chapter 18 Amines And Neurotransmitters
Match the name or structure with its functional group Each molecule has only one functional group My choices are alkane, alcohol, alkyne, carboxylic acid, alkene, aldehyde, ketone, ester, and ether 1 2propanol alcohol 2 social studies An interest group that focuses on policy benefits for senior citizens would be an example of a(n) aIn traditional names various qualifiers are used to label isomers, for example, isopropanol (IUPAC name propan2ol) is an isomer of npropanol (propan1ol) The term moiety has some overlap with the term "functional group"The functional group contained in the compound CH3CH2OCH2CH3 is a(n) ether The functional group contained in the compound CH3CH2CH=CHCH3 is a(n) alkene What is the name of the alkyl group CH3 CH2 CH2 ?



How To Name Using Iupac Guidlines




Amides
CH 3 CH 2 Cl Chloroethane or ethyl chloride Nucleophilic subsitution;2 benzylamine NH 2 aniline N diisopropylethylamine Hunig's base Amides R'(C=O)NH 2 primary R'C(=O)NHR secondary R'(C=O)NR 2 tertiary CH 3 NH 2 O acetamide Ph NH 2 O benzamide H N(CH 3) 2 O N,Ndimethylformamide DMF N O Nmethylpyrrolidone N H piperidine N H pyrrolidine O N H morpholine Azo Ph N N Ph azobenzene Carbamates (urethanes) Et 2N OMe O methyl N,Ndiethylcarbamate Me 2N Cl O N,Ndimethylcarbamoyl chloride Ph N NThe names of alkenes and alkynes are based on the names of alkanes, but the suffix of the name varies to indicate the functional group present For example, a twocarbon compound containing a double bond, CH 2 =CH 2 , is called ethene rather than ethane



What Is The Iupac Name Of This Compound Ch3ch2ch2co N Ch3 2 Quora




10 2 Functional Groups Chem 1114 Introduction To Chemistry
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 NHCH 3 Solution There is only one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen atom, so the amine is primary A group of three carbon atoms (a propyl group) is attached to the NH 2 group through an end carbon atom, so the name is propylamine There are two methyl groups and one ethyl group on the nitrogen atom(functional group) Generic formula Example Example name propanol Alkyl halide R X fluoride chloride bromide CH3CH2COCH3 methyl propanoate O CH3CH2CN(CH3)2 N,Ndimethylpropanamide Title functional_groupscdx AuthorFAMILY FUNCT GROUP EXAMPLE SUFFIX Hydrocarbons Alkane or (only single bonds) ethane –aneH Alkene C ethylene C H2CCH C HCCH C C C C C C CX H3CCl COH H3COH COC H3COCH3 CN H3CNH2 CCH O HCC O OH CCC O HCC O CH3 CCO O H HCCOCH3 CCOC O C H3CC O OCCH3 CCOC HCCOCH3 CCN O HCC O NH2 C C C C C C H H HH H Title Microsoft Word Functional Groups




Amine Chemical Compound Britannica
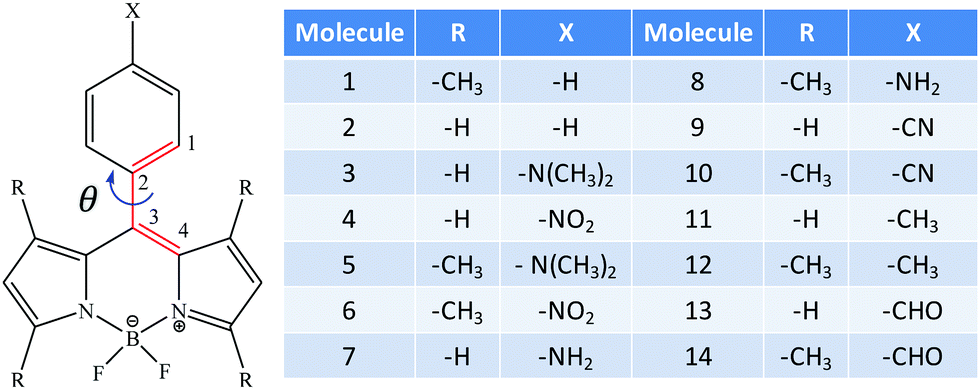



Interplay Of Twist Angle And Solvents With Two Photon Optical Channel Interference In Aryl Substituted Bodipy Dyes Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing
O C OH (with an oxygen double bonded above the Carbon) A carboxylic acid is named in the IUPAC system by replacing the e in the name of the parent alkane with ________ oic acid The functional group in acetic acid is called the ________ carboxyl group The IUPAC name of this compound is ________ A butanol line structure with a chlorineElimination Aryl halides C 6 H 5 Cl Chlorobenzene Electrophilic & nucleophilic aromatic substituion Alcohols CH 3 CH 2 OH Ethanol or ethyl alcohol Dehydration;Manufacturer Name Melting Point (°C) Physical Form Purity Agency Format Functional Group Industry Markush Class Markush Group Organoleptic Class Organoleptic Subclass Special Grade analytical standard (CH 3)COO m CH 2 CH 2 O n CH 3 Product Number Product Description SDS;




Functional Groups




Stereochemistry Isomers Are Different Compounds Prezentaciya Onlajn
Example 9 Name and classify each compound 1 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 NH 2 2 3 CH 3 CH 2 NHCH 2 CH 3 4 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 NHCH 3 Solution There is only one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen atom, so the amine is primaryContaining functional group 4 2 Suffix basic name derived by adding ending of major functional group (FG) 3 2° amine N CH3 H3C H3C trimethylamine 3° amine N H H H ammonia N CH3 H3C H3C trimethylammonium ion 4° ammonium (salt) H If add four groups everything changes!If not, give the correct names 1Methyoxyethan2ol Medium View solution Fill in the blanks The functional group in an alcohol is _____ and its suffix in IUPAC system is _____ Medium View solution View more Learn with content Watch learning videos, swipe through stories, and browse through concepts Concepts > Videos >




Functional Groups
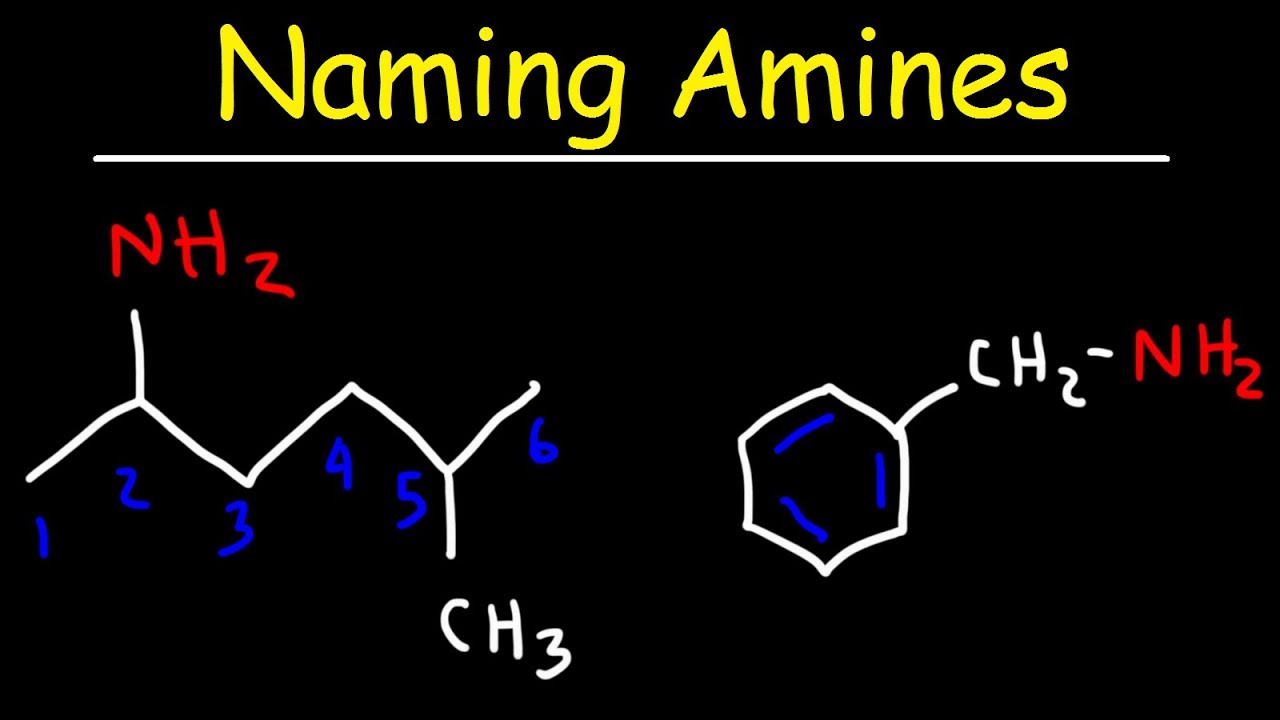



Naming Amines Iupac Nomenclature Common Names Youtube
The smaller alkyl group forma a part of the Nalkyl group while the larger alkyl groupIt is a 3^ Amine as two methy group is directly attached to N Since there are 4 carbon in the longest chain so it is butane



1
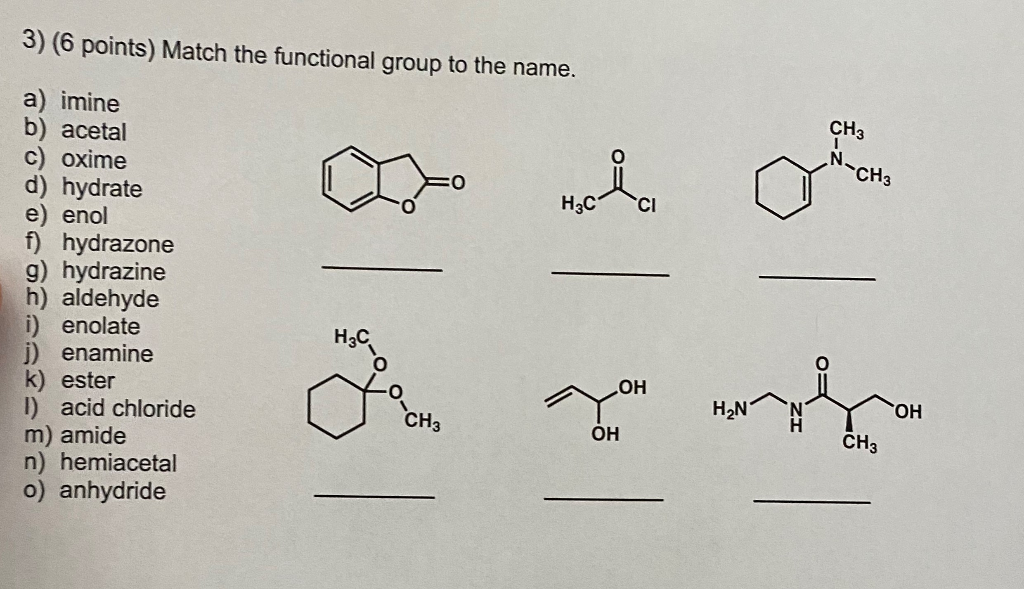



3 6 Points Match The Functional Group To The Name Chegg Com
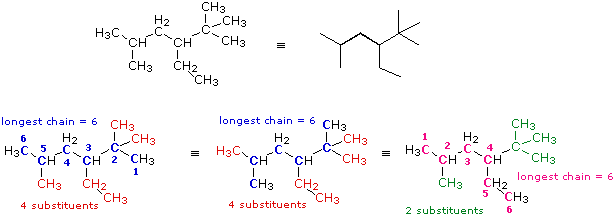



Nomenclature Examples




10 2 Functional Groups Chem 1114 Introduction To Chemistry



Http Www Chem Latech Edu Upali Chem121 Notes C17 121 Pdf



Www Mattliden Fi Media Kunena Attachments 2764 Answerstorevisiontest Pdf




Chemistry Chapter 8 Amines Ppt Download



Q Tbn And9gctjhuexwf0ja9nvz9rctjtjcyjlvv2kbm1foiuzw8tnl1kpekwt Usqp Cau
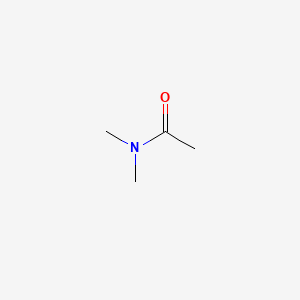



N N Dimethylacetamide C4h9no Pubchem



1 6 Functional Groups Chemistry Libretexts



What Is The Iupac Name Of Ch3ch2ch2n Ch3 2 Quora




Structural Isomerism Chain Positional Functional Group Isomers Tautomerism Possible Number Structures From Molecular Formula A Level Gce As Organic Chemistry Revision Notes



Functional Group



Organic Nitrogen Compounds Iii Secondary And Tertiary Amines




Amines And Nitro Compounds Vladimira Kvasnicova Amines Organic Derivatives Of Ammonia In Which One Or More Of The Hydrogen Atoms Is Replaced By An Ppt Download




Functional Groups Ck 12 Foundation




The Electrostatic Potential Map Of Para Methoxy Styrene On Three Download Scientific Diagram



Functional Groups




Eth Yne C 2 H 2 Prop Yne C 3 H 4 Pdf Free Download




Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Of Organic Compounds Functional Groups



Carboxylic Acid Reactivity



People Ok Ubc Ca Pphillips Iupac organic nomenclature alkanes examples Pdf




Asymmetric Catalysis By Architectural And Functional Molecular Engineering Practical Chemo And Stereoselective Hydrogenation Of Ketones Noyori 01 Angewandte Chemie International Edition Wiley Online Library



What Is The Iupac Name Of Ch3n Ch3 Ch3 Quora




Dynamics Functional Groups Flashcards Quizlet



Functional Groups Chemistry Drills




Ch105 Chapter 9 Organic Compounds Of Oxygen Chemistry
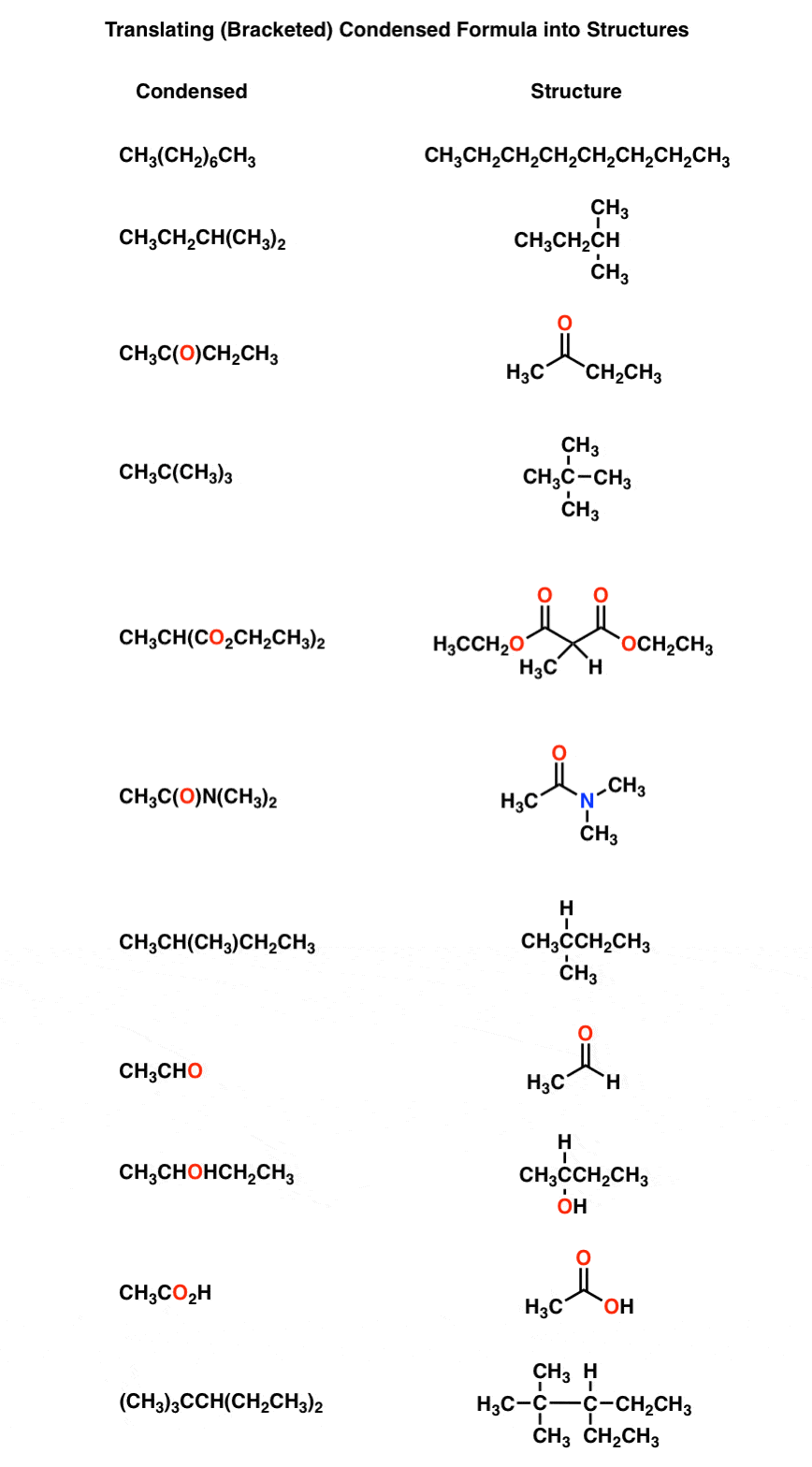



Condensed Formulas Deciphering What The Brackets Mean Master Organic Chemistry




Nomenclature In Organic Chemistry



Laney Edu Cheli Fossum Wp Content Uploads Sites 210 19 01 Naming Amines And Amides Rules Pdf




Ch3 Ch2 Ch2 Co N Ch3 2 How To Name This Compound Iupac Chemistry Coordination Compounds Meritnation Com
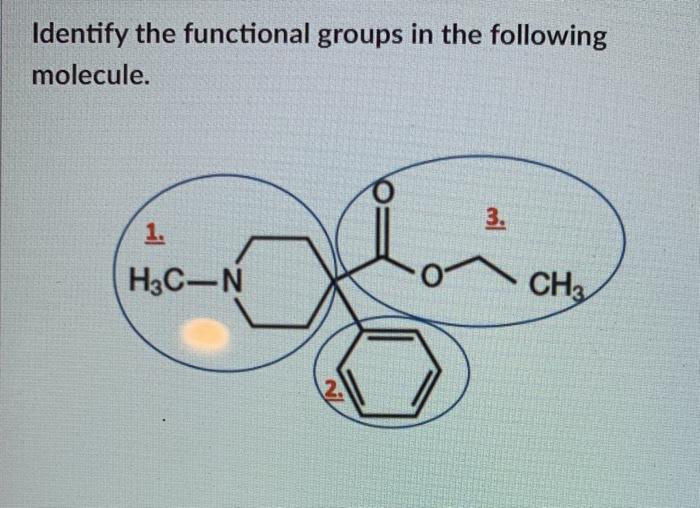



Identify The Functional Groups In The Following Chegg Com
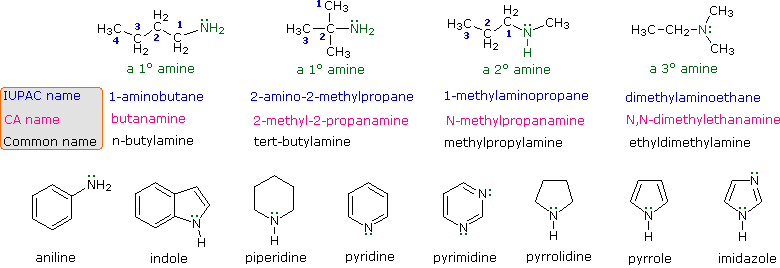



Amine Reactivity




Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Of Organic Compounds Functional Groups



Q Tbn And9gcrq9cdps4c0 Mvg 8cauin4vasr6voa5cqqxbdmiqlwy73ekxfm Usqp Cau




How To Name Ch3och2ch3 Youtube




Chapter 25 Section 4




Structural Isomerism Chain Positional Functional Group Isomers Tautomerism Possible Number Structures From Molecular Formula A Level Gce As Organic Chemistry Revision Notes




Functional Group Names Properties And Reactions Chemistry Master




Iupac Naming And Formulae Organic Molecules Siyavula



Laney Edu Cheli Fossum Wp Content Uploads Sites 210 19 01 Naming Amines And Amides Rules Pdf



Http Www Whsd Net Userfiles 15 Functional groups Functional groupsonline Pdf
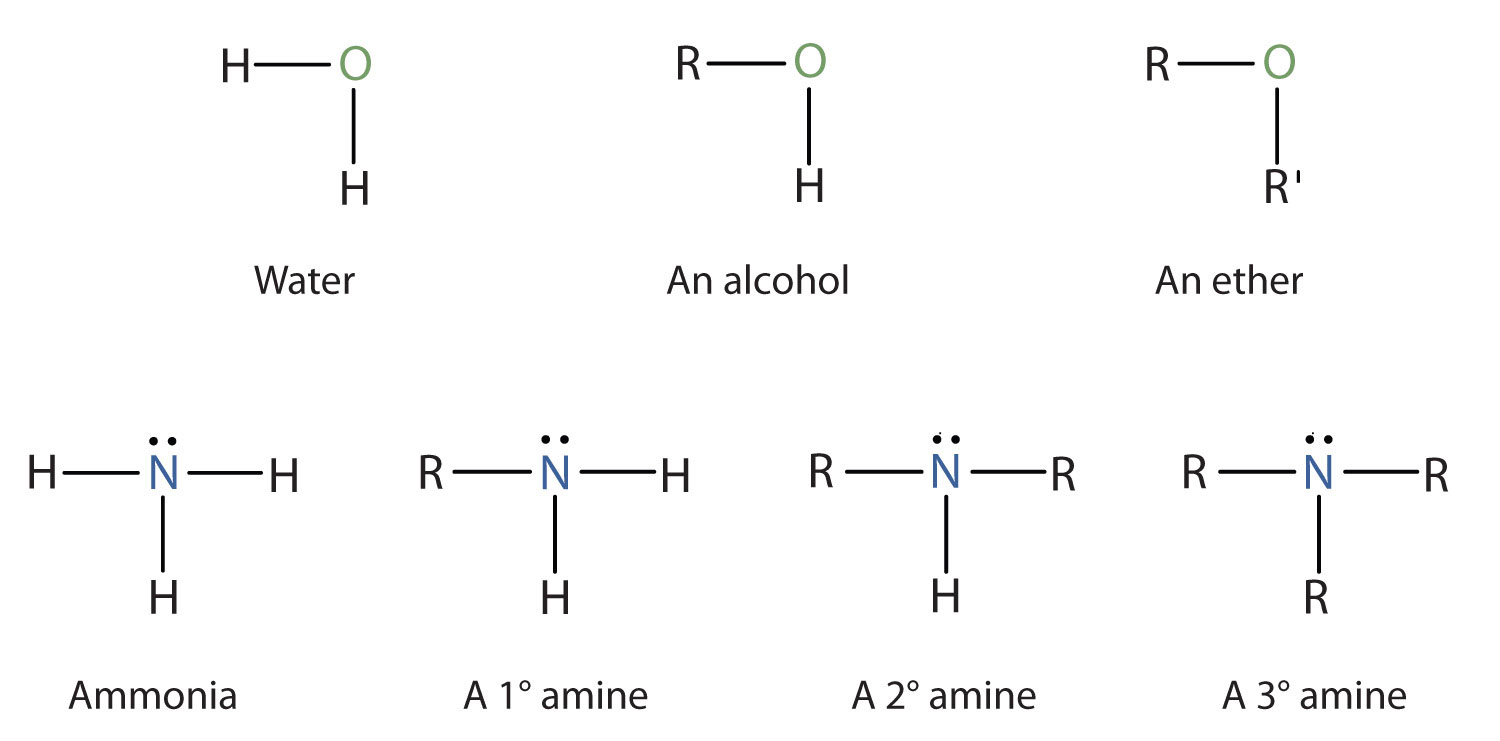



Amines Structures And Names
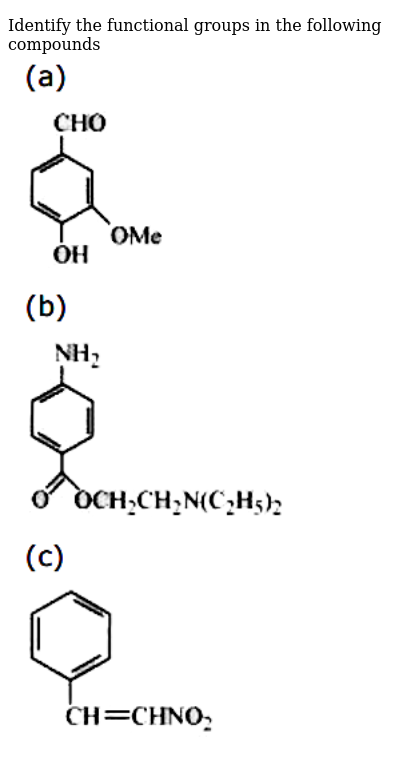



Identify The Functional Groups In The Following Compounds Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Chm V02 Xi C12 E01 008 Q01 Png Width 80



Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 0 387 3 3 Pdf



Http Www Chymist Com Organic nomeclature Pdf
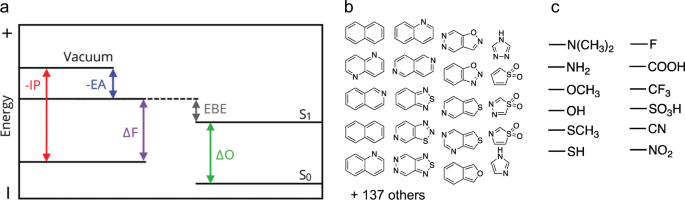



Mapping The Optoelectronic Property Space Of Small Aromatic Molecules Communications Chemistry



Acikders Ankara Edu Tr Mod Resource View Php Id 6507



Imine Wikipedia
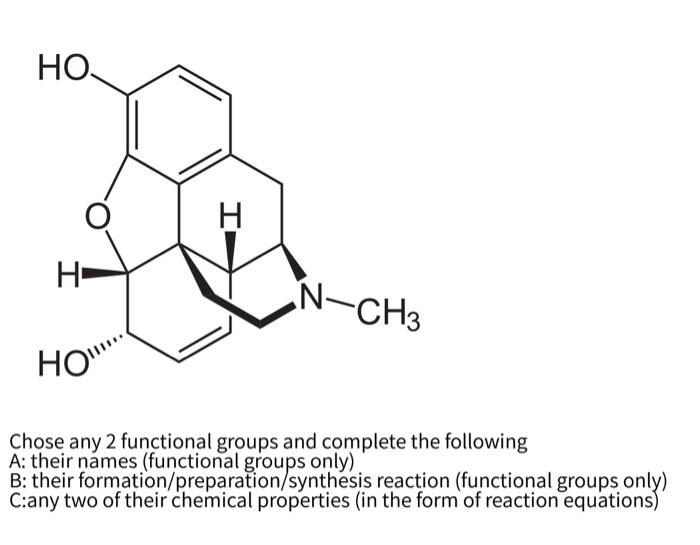



Ho I N N Ch3 How Chose Any 2 Functional Groups And Chegg Com
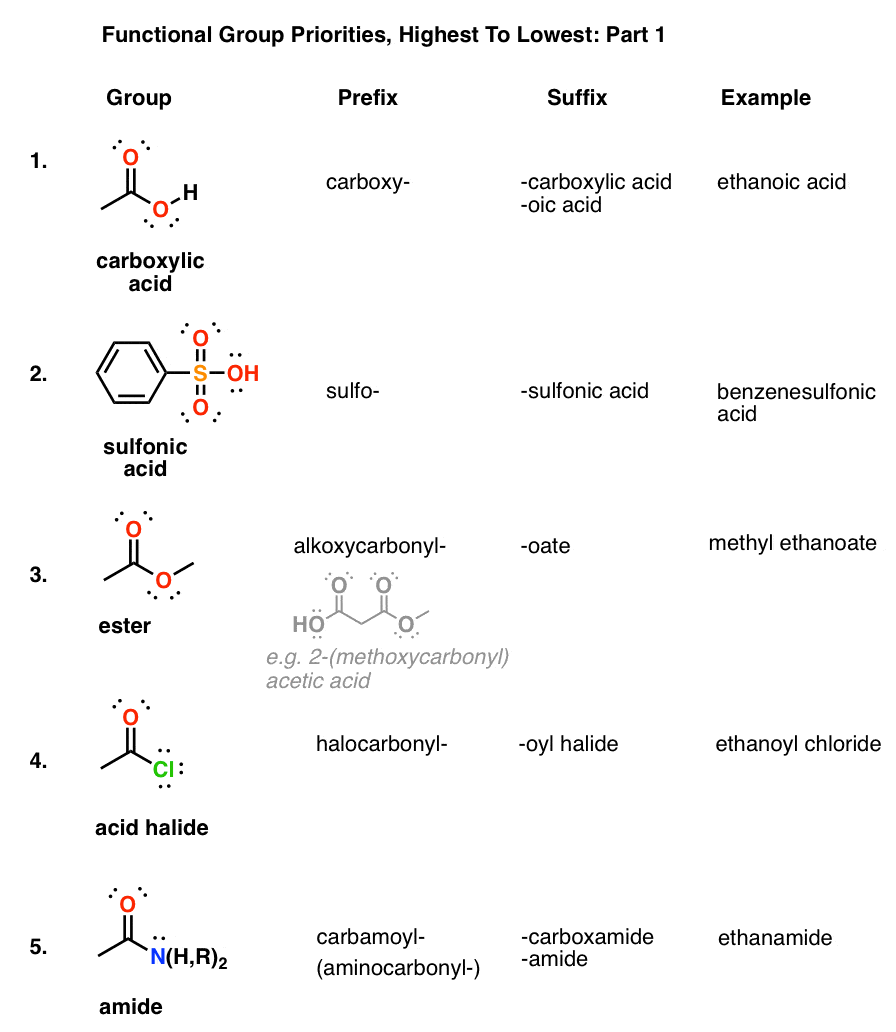



Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature Master Organic Chemistry
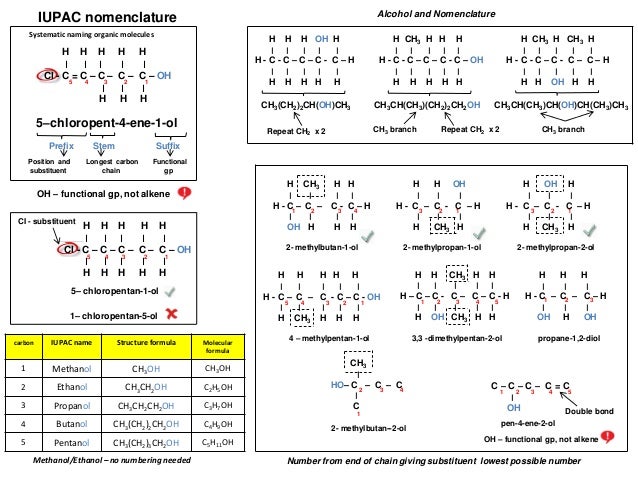



Ib Chemistry On Organic Nomenclature And Functional Groups



Http Www Chymist Com Organic nomeclature Pdf




Methoxy Group Wikipedia
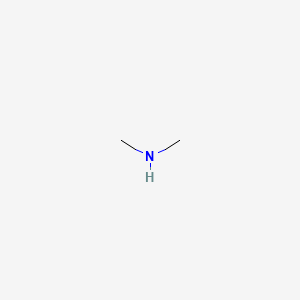



Dimethylamine Ch3 2nh Pubchem
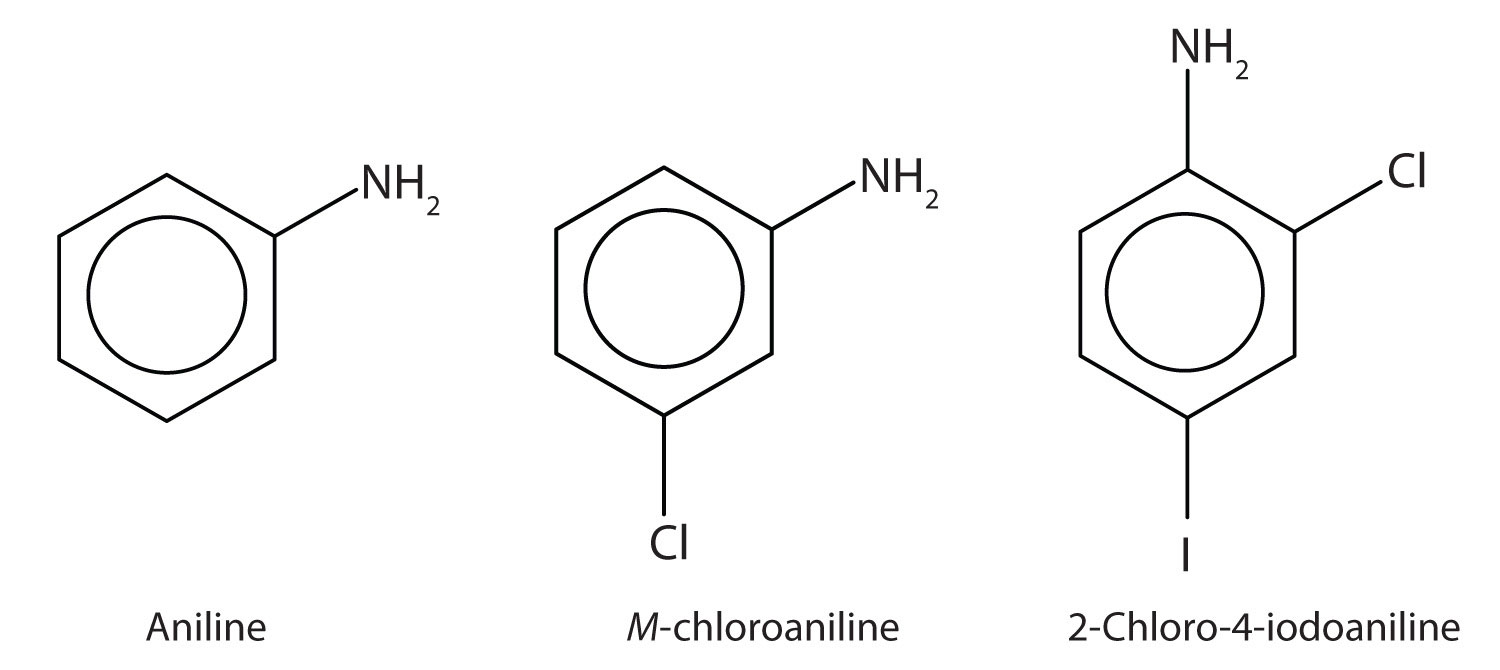



Amines Structures And Names




1 1 Dichloroethane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Synthesis Of Mono N Methyl Aromatic Amines From Nitroso Compounds And Methylboronic Acid Abstract Europe Pmc



Hal Archives Ouvertes Fr Hal Document




Functional Groups Video Khan Academy
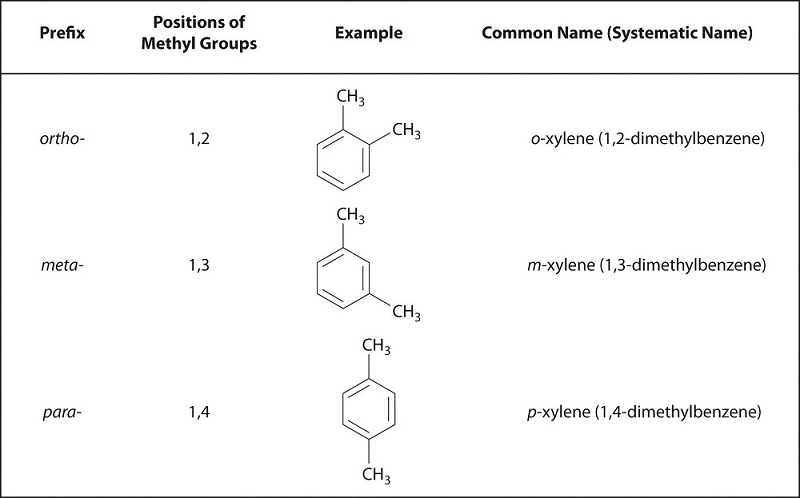



24 1 Functional Groups And Classes Of Organic Compounds Chemistry Libretexts



Ppt Organic Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Of Organic Compounds Functional Groups




Some Organic Compounds Are Given I Ch3 Ch2 Ch2 Ch2 Ch3 Ii Ch3 Ch2 O Ch2 Ch3 Iii Ch3 Ch2 Ch2 Ch2



Functional Group




For Each Of The Following Compounds Write A Condensed Formula And Also Their Bond Line Formula A Hoch 2 Ch 2 Ch 2 Ch Ch 3 Ch Ch 3 Ch 3 B Nequivc Overset Oh Overset Ch Cequivn



Solved Please Answer The Whole Thing And Please Make Sure That You Are 100 Sure Of Your Answers Thank You Course Hero



Chem 331 Homework 2 Answers



Design And Synthesis Of Chromophores And Polymers For Electro Optic And Photorefractive Applications Nature




Functional Group Names Properties And Reactions Chemistry Master



1



Functional Groups



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿